Thank you for your
attention on Yesheng !
Types of Tubular Reactors
A tubular reactor is a type of continuous reactor with a tubular shape and a high length-to-diameter ratio. These reactors can be very long; for instance, the length of polyethylene reactors can be measured in kilometers. The structure can consist of a single tube or multiple tubes arranged in parallel. It can be an empty tube, such as in tubular cracking furnaces, or a packed tube filled with particulate catalysts for multiphase catalytic reactions, like in a shell-and-tube fixed-bed reactor. Typically, when the flow of reactants is in a turbulent state, the length-to-diameter ratio of an empty tube is greater than 50; for packed sections, the ratio of length to particle diameter is greater than 100 for gases and 200 for liquids. The flow of materials can be approximated as plug flow.
Classification of Tubular Reactors
1、Horizontal Tubular Reactors
These reactors are made by connecting seamless steel pipes with U-shaped tubes. This structure is easy to manufacture and maintain. High-pressure reactor pipelines use standard groove butt-welded steel flanges that can withstand pressures of 1600-10,000 kPa. When using lens-type steel flanges, they can withstand pressures up to 10,000-20,000 kPa. For example, high-pressure polyethylene reactors can reach pressures up to 280 MPa.
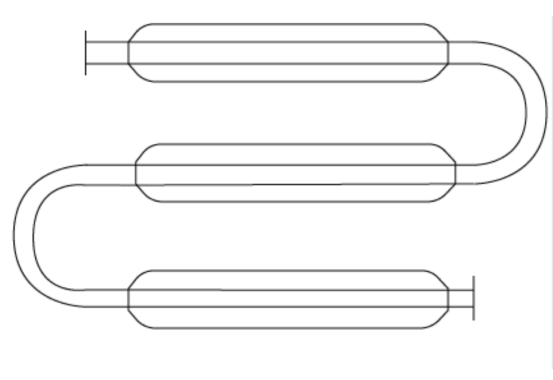
2、Vertical Tubular Reactors
Vertical tubular reactors are used in processes such as liquid-phase amination, liquid-phase hydrogenation, and liquid-phase oxidation. Vertical tubular reactors can be single-pass or have a central insert tube design.
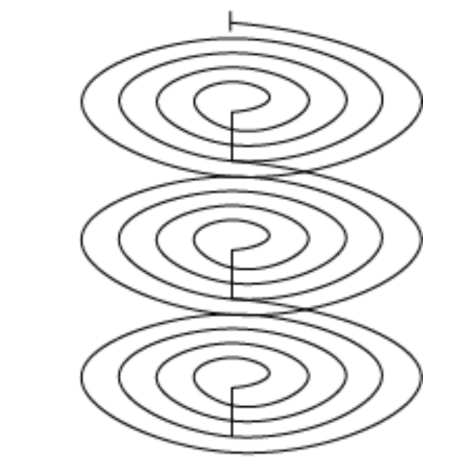
3、Coil Tubular Reactors
These are tubular reactors formed into coils, making the equipment compact and space-saving. However, maintenance and cleaning of the pipes are relatively difficult.
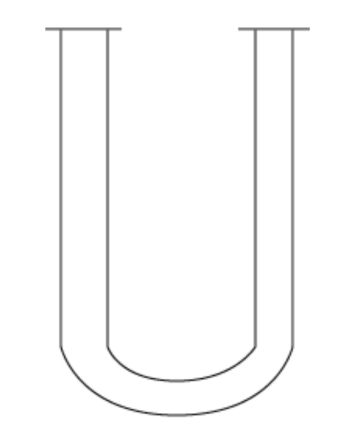
4、U-Shaped Tubular Reactors
U-shaped tubular reactors have porous baffles or stirring devices inside the tubes to enhance heat and mass transfer processes. The large diameter of the U-shaped tube allows for longer residence times of the material, making it suitable for reactions with slower reaction rates.
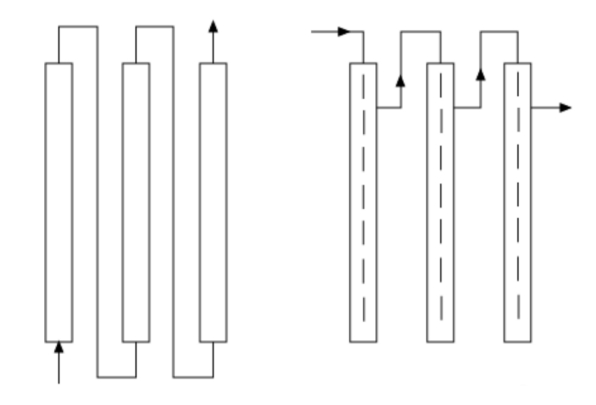
5、Multi-Tube Parallel Tubular Reactors
Tubular reactors with a multi-tube parallel structure are generally used for gas-solid phase reactions. For example, in the production of vinyl chloride, hydrogen chloride gas and acetylene gas react in a multi-tube parallel reactor filled with solid-phase catalysts. Similarly, in ammonia synthesis, a mixture of nitrogen and hydrogen gases reacts in a multi-tube parallel reactor containing a solid-phase iron catalyst.

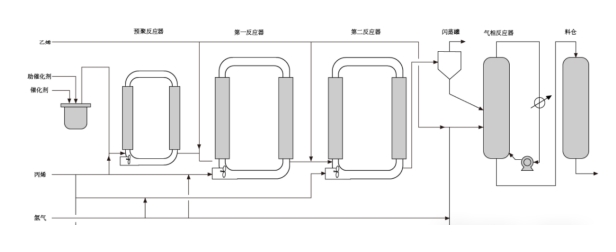
6、Series Tubular Reactors
Multiple tubular reactors can be connected in series, such as in the polypropylene production process. The Spheripol process flow diagram for polypropylene preparation includes a pre-polymerization reactor, a first reactor, and a second reactor connected in series.
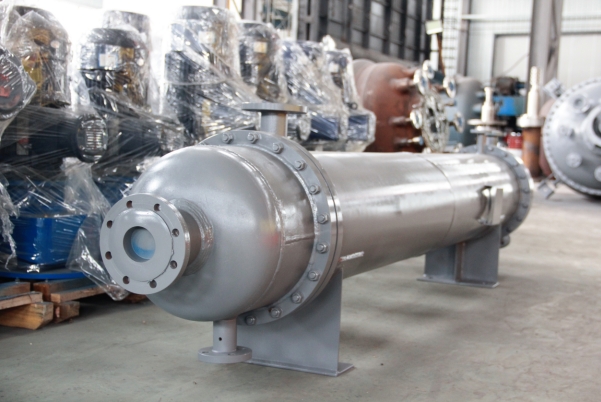
Differences Between Tubular Reactors and Stirred Tank Reactors
Tubular reactors are classified as plug flow reactors, whereas stirred tank reactors are continuous stirred-tank reactors (CSTRs). The residence time in tubular reactors is relatively short, while it is longer in stirred tank reactors. In terms of removing reaction heat, it is more challenging in tubular reactors, whereas it is easier in stirred tank reactors, which can have external jackets or internal coils. Sometimes a combined tubular and stirred tank reactor system is used, where the material exits the bottom of the stirred tank reactor and flows through an external loop into a tubular reactor before returning to the stirred tank reactor. An external loop cooler can be set up after the tubular reactor to control temperature. The reactants enter through the inlet of the tubular reactor or the inlet of the external circulation pump, and the product overflows from the top of the stirred tank reactor, thereby utilizing both types of reactors.

Characteristics of Tubular Reactors
1、Since the residence time of reactant molecules in the reactor is equal, the concentration of reactants and the chemical reaction rate at any point in the reactor do not change over time, but only vary with the tube length.
2、Tubular reactors have a small volume, large specific surface area, and large heat transfer area per unit volume, making them particularly suitable for reactions with significant heat effects.
3、Due to the fast reaction and flow rates in tubular reactors, their production capacity is high.
4、Tubular reactors are suitable for large-scale and continuous chemical production.

 English
English  日本語
日本語  한국어
한국어  français
français  Deutsch
Deutsch  русский
русский 























































































